Industry
- PRESENT SITUATION
- FORECAST IN THE SHORT AND MID TERM
- LOCATION OF THE INDUSTRIAL ACTIVITY
- INUDSTRIAL DEMAND
- POLLUTING DICHARGES TO THE INDUSTRY
- OTHER INFORMATION AND DOCUMENTS OF INTEREST
The hydric requirements in this sector are related to the use of water for industrial production that includes the specific use in products and manufacturing processes, packaging, conservation, personal hygiene, maintenance, security in the facilities, etc.
The water use in the industry causes quantitative and qualitative challenges (extractions and spilled)
PRESENT SITUATION
Industry is the sector most profitable economically in the water use. The water productivity in the Spanish industry is around 100 euros by cubic meter used (each cubic meter of water is associated with the generation of 100 euros of wealth).
The amount of water used in industrial processes is estimated in 965 cubical hectometres, occupying the third position between the most significant water uses, then irrigation and domestic supply.
The VAB represents the economic value generated by unit production and is obtained as a balance of production account. The difference between the production of services and intermediate consumption.
It is possible consider to the industry like the sector with the highest rate of growth in relative terms with a increase of 3.5 % per year.
The following figure and graph, represent the Value Added of Industry by regions
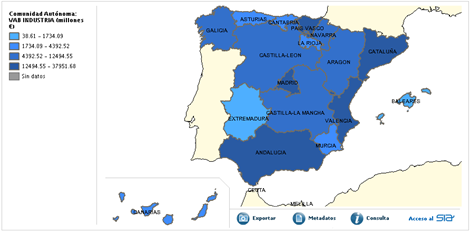

Figure 1: Value added of Industry. Source: Sistema Integrado de Información del Agua.SIA
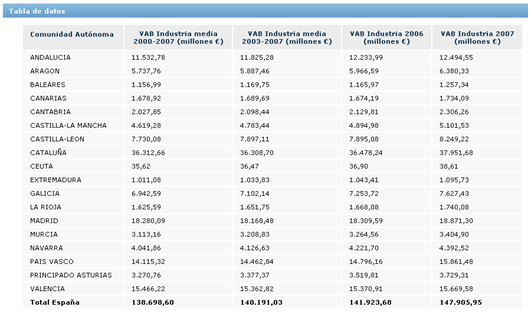

Figure 2: Added value of industry by regions. Source: Sistema Integrado de Información del Agua. SIA
FORECAST IN THE SHORT AND MID TERM
The water productivity in the Spanish industry will increase at a rate of half point (despite to consider constant the technology), this situation would not be enough to offset the economic growth of the sector producing with a net increase in water demand.
LOCATION OF THE INDUSTRIAL ACTIVITY
Between water uses, the industrial activity is the activity that presents a higher territorial concentration.
A quarter of the Spanish industrial production is located in the Catalonia river basins, one of the smaller river basins, the Community of Madrid reaches the 10% of the industrial production and the Tajo river basin the 13%, the other 25% is distributed between the Ebro and Jucar river basin. Pressure on the territory is concentrated around Barcelona and Madrid and the large industrial parks in the Ebro Valley, the Basque Country and Levant.
- Internal river basins of the Basque Country: the metallurgical industry, machinery and mechanical equipment is in these river basins, the second in national importance although there is located only 7% of the industrial production.
Internal river basin of Catalonia: the 40% of the production of the Spanish Chemical Industry are located, 36% of the Textile, 30% of the machinery production and 28% of the graphical arts. - Tajo river basin: Madrid, ocupies an important place with the 29% of the electronic production and in the papel industry and graphics arts and less of 20% of chemical industry.
- Júcar river basin: this river basin concentrates the 27% of the nonmetalists mineral industry of and the 22% of textil industry, leather and footwear.
The exception to the spatial concentration of the industry, occurs in the sector of foods, drinks and tobaccos, that contribute with the 15% of the industrial production. The municipalities more specialized are situated around the agrarian regions with more productivity of the river basins (zones of vineyard in La Rioja and La Mancha, the Valley of the Jerte, the Region of Murcia…)
INDUSTRIAL DEMAND
In global terms the water demand of the industry does not suppose a great volume, but the discharges generated by the industrial activities have a very important impact on the waters state.
The industrial demand is influenced by socio-economic characteristics like the number of industrial establishments, the employment, the production, the raw materials, the productive processes, and the application of new technologies to improve the water use and the possibilities of water reusability within the industrial process.
The following map shows the spatial distribution of these water demands in mm / year, associated with great concentrations of industrial activity.
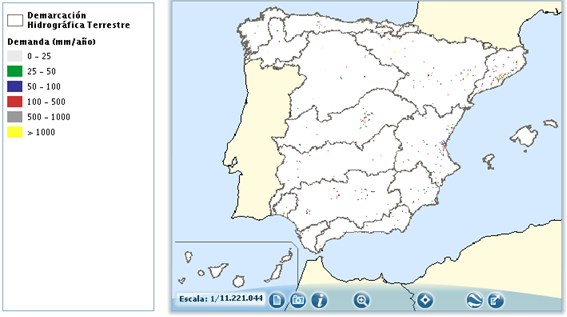

Figure3: Distribution of water demands associated with great concentrations of industrial activity. Source: Sistema Integrado de Información del Agua. SIA
The following table shows the volumes of water collected by the companies according to the National Code of Economic Classification (NACE)

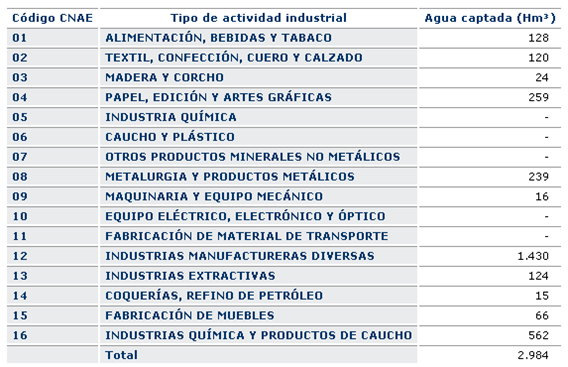
Figure4: Volumes of water collected by the companies according to NACE. Source: Sistema Integrado de Información del Agua. SIA
POLLUTING DISCHARGES OF THE INDUSTRY
The typical composition of polluting discharges is different in the different productive processes to which water quality is submitted.
About to the type of discharges, the food sector, for example, produces effluents with a composition worse than the Spanish average for all pollutants except heavy metals and toxic chemicals. In the chemical industry, emissions have a concentration higher to the industrial discharges in all the quality parameters.
The following table and graph shows the volume of wastewater generated by industries according to the National Code of Economic Classification (NACE)
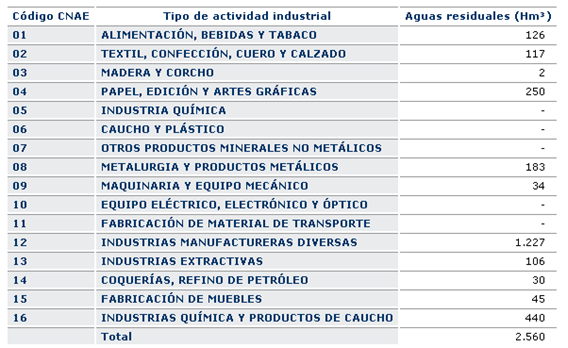

Figure5: Wastewater generated by the industry in 1999. Source: Sistema Integrado de Información del Agua. SIA